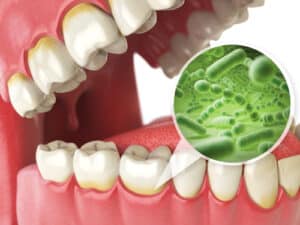
In a study published last month in the International Journal of Oral Science, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that a common oral pathogen can stop cardiac muscle cells from repairing themselves after a heart attack caused by coronary heart disease.
Heart attacks occur when blood flow in the coronary arteries is blocked, resulting in an inadequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle, and ultimately death of cardiac muscle cells. To prevent this, cardiac muscle cells use a process known as autophagy to dispose of damaged cellular components, keeping them from causing cardiac dysfunction. The oral pathogen inhibits the heart muscle cells from this necessary repair.
If you, your family, or friends need dental care, we would be honored to provide you with state-of-the-art dental care in our modern dental practice. Refer someone you love to someone you trust!
Presented as a service to the community by Doctors Hoover and Yanda,
39 Milford Drive, Hudson, Ohio 44236. 330-650-0360.

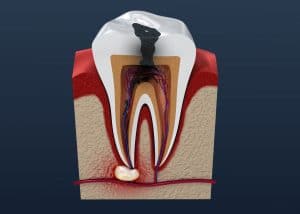 An abscessed tooth is an infection caused by tooth decay, periodontal disease or a cracked tooth. These problems can allow bacteria to enter the pulp (the soft tissue of a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue) and can lead to pulp death. When pus builds up it forms a pus-pocket called an abscess. If the abscess is not treated, it can lead to a serious infection in the jawbone, teeth and surrounding tissues.
An abscessed tooth is an infection caused by tooth decay, periodontal disease or a cracked tooth. These problems can allow bacteria to enter the pulp (the soft tissue of a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue) and can lead to pulp death. When pus builds up it forms a pus-pocket called an abscess. If the abscess is not treated, it can lead to a serious infection in the jawbone, teeth and surrounding tissues. When compared with nondrinkers, men and women who had one or more alcoholic drinks per day had an overabundance of oral bacteria linked to gum disease, some cancers, and heart disease. Alcohol drinkers also had fewer bacteria known to check the growth of other, harmful germs. These are the main findings of a study published in the journal Microbiome.
When compared with nondrinkers, men and women who had one or more alcoholic drinks per day had an overabundance of oral bacteria linked to gum disease, some cancers, and heart disease. Alcohol drinkers also had fewer bacteria known to check the growth of other, harmful germs. These are the main findings of a study published in the journal Microbiome.